Background
The Air Quality Index or AQI is a numerical system that indicates the quality of air in a given area. It helps people understand how clean or polluted the air is and what health impact it may have.
In India, the AQI is managed by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
Objectives
-
To provide daily information about air quality to the public.
-
To alert sensitive groups such as children, elderly people, and those with heart or respiratory problems.
-
To assist policymakers in framing air pollution control strategies.
Main Pollutants included in Indian AQI
-
Particulate Matter PM10
-
Fine Particulate Matter PM2.5
-
Nitrogen Dioxide NO2
-
Sulphur Dioxide SO2
-
Carbon Monoxide CO
-
Ozone O3
-
Ammonia NH3
-
Lead Pb
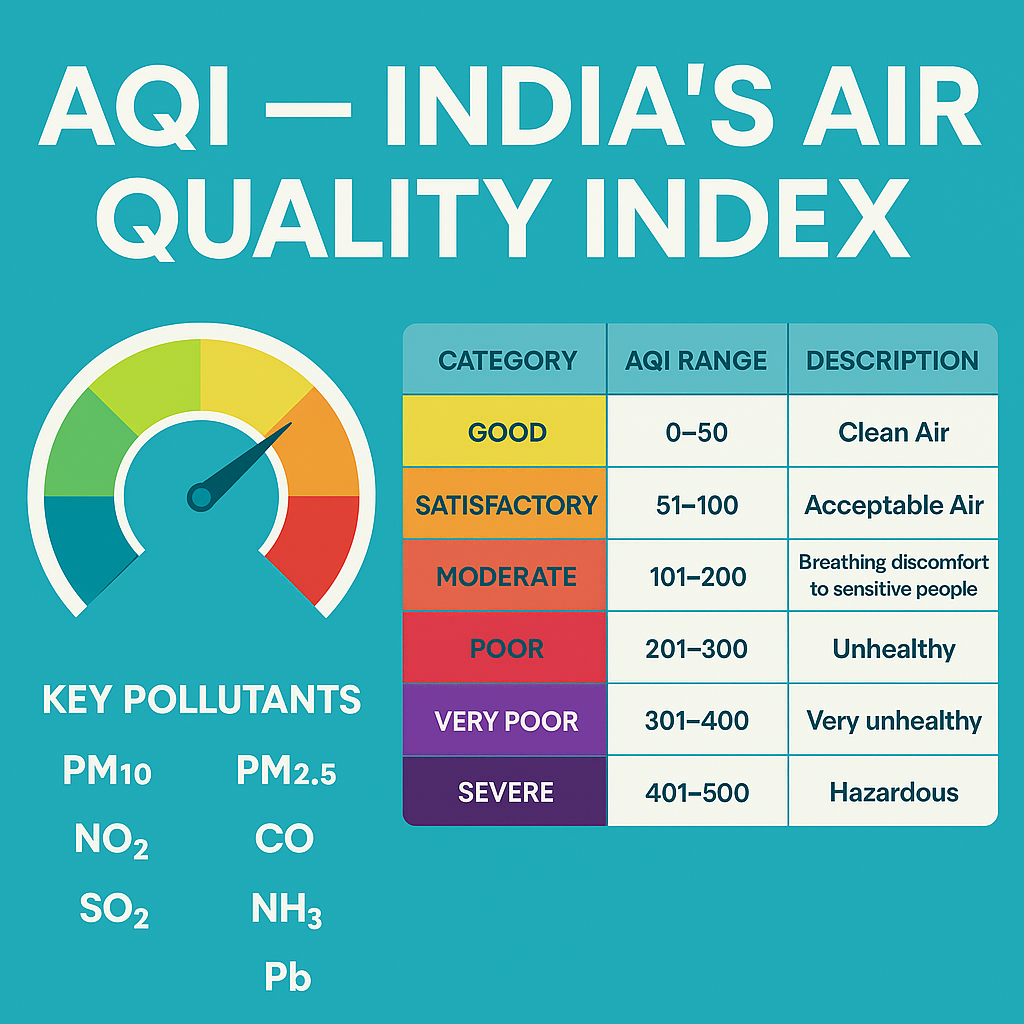
AQI Categories according to CPCB
Good – AQI 0 to 50 – Clean air – No effect on health
Satisfactory – AQI 51 to 100 – Acceptable air – Minor discomfort to sensitive people
Moderate – AQI 101 to 200 – Polluted air – Possible breathing difficulty
Poor – AQI 201 to 300 – Unhealthy – May affect lungs
Very Poor – AQI 301 to 400 – Highly polluted – Risk of respiratory illness
Severe – AQI 401 to 500 – Extremely dangerous – Serious health impact






Comments (0)
Leave a Comment